Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem
The alternate exterior angles theorem states that if a transversal intersects or cuts two lines that are parallel, then the alternate exterior angles are congruent or equal.
In the figure below, the red line is the transversal or the line that cuts or intersects the two blue lines that are parallel. Therefore, the alternate exterior angles shown in orange, named 3 and 4, are congruent or equal.
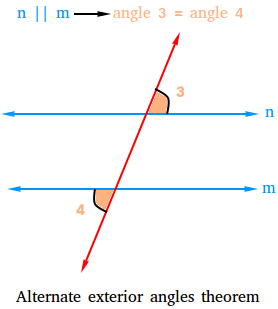
Examples showing how to use the alternate exterior angles theorem
1.
Use the figure below to find the measure of angle y.
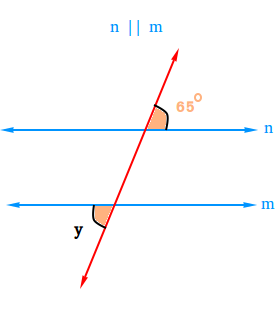
Since line n is parallel to line m, angle y has the same value as the angle whose value is 65 degrees.
y = 65 degrees.
2.
Use the figure below to find the value of b.
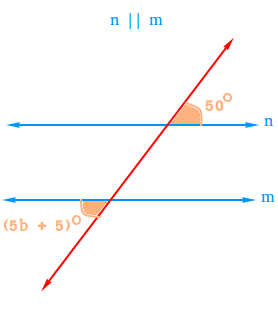
Since line n is parallel to line m, (5b + 5)0 has the same value as the angle whose value is 50 degrees.
5b + 5 = 50
5b + 5 - 5 = 50 - 5
5b = 45
b = 9