Become math lovers!
What does variable mean in algebra ? Definition and examples.
In algebra, a variable is usually a letter or symbol that stands for an unknown number or quantity. You could use a variable to do the following:
- To represent an unknown number that cannot vary.
- To represent an unknown number that can vary.
Unknown number that cannot vary
For example, in y + 8 = 10 and ? - 2 = 4, y and ? are used to represent unknown numbers that do not vary.
y is equal to 2 since 2 + 8 = 10 and y cannot vary. In other words, y can never be equal to anything else.
? is equal to 6 since 6 - 2 = 4 and ? cannot vary either.
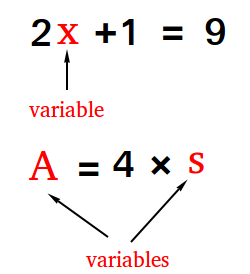
Unknown number that can vary
The formula to get the perimeter of a square is p = 4 × s
If s is the length of one side of the square, the perimeter varies as s varies.
For example, if s = 2, p = 4 × s = 4 × 2 = 8
If s = 3, p = 4 × s = 4 × 3 = 12